Contents
- 1 GRADES / TYPES OF CEMENT?
- 2 WHAT IS 33 GRADE CEMENT?
- 3 WHAT IS 43 GRADE CEMENT?
- 4 WHAT IS 53 GRADE CEMENT?
- 5 PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF VARIOUS TYPES OF CEMENT?
- 6 CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF VARIOUS TYPES OF CEMENT?
- 7 TYPE OF CEMENT RECOMENDED BASED ON SO3 level in SOIL?
- 8 WHAT IS THE NEW TECHNOLOGICAL – CEMENT IMPACT ON OPC CEMENT?
- 9 WHAT IS ULTRA HIGH-PERFORMANCE CONCRETE?
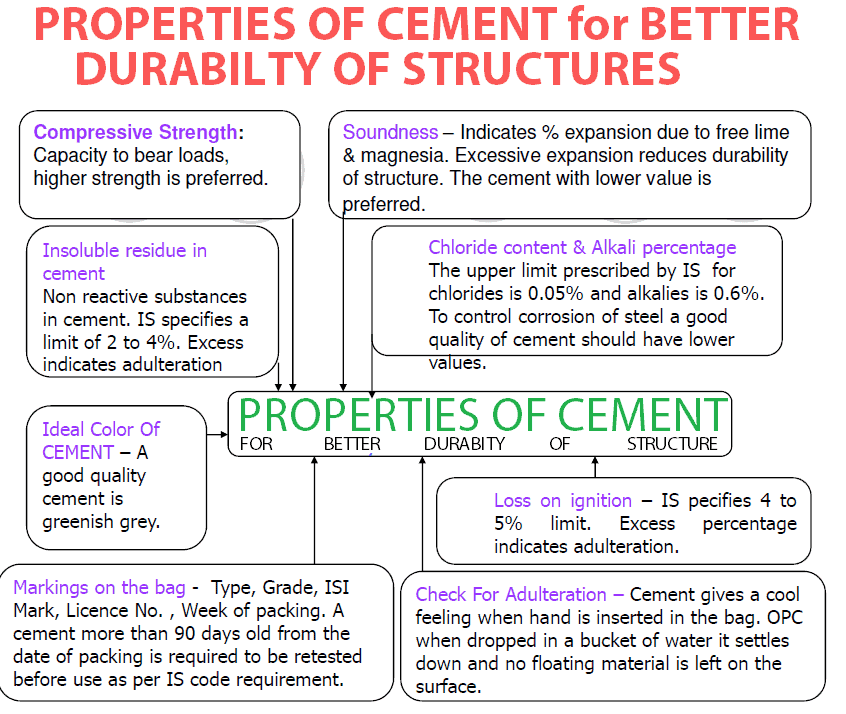
- 10 WHAT ARE THE PROPERTIES OF CEMENT?
GRADES / TYPES OF CEMENT?
Cement is known to be a prominent ingredient that contains mortar, concrete, and plaster. The grade and strength of cement get to be determined by the concrete mixture of these ingredients.
If you plan to build a house in Bangalore and think of which cement must be used for house construction, this article will help you!
| TYPES OF CEMENT and PROPERTIES OF CEMENT 33 GRADE CEMENT 43 GRADE CEMENT 53 GRADE CEMENT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TYPES OF CEMENT | 33 Grade CEMENT IS 269:1989 |
43 Grade CEMENT IS 8112:1989 |
53 Grade CEMENT IS 12269:1987 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: Minimum compressive strength, N/mm2 |
N/mm2 | N/mm2 | N/mm2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 day 7 day 28 day |
16 22 33 |
23 33 43 |
27 37 53 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fineness Minimum specific surface (Blaine’s air permeability) m2/kg |
225 | 225 | 225 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Setting time, minutes initial, minimum final, maximum |
30 600 |
30 600 |
30 600 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Soundness, expansion (Le Chatelier test, mm), maximum Autoclave test for MgO, percent, maximum |
10.0 0.8 |
10.0 0.8 |
10.0 0.8 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CHEMICAL PROPERTIES: Loss on ignition, per cent, maximum Insoluble residue, per cent, maximum Magnesia MgO, per cent, maximum |
5.0 4.0 6.0 |
5.0 2.0 6.0 |
4.0 2.0 6.0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SO3, per cent, maximum for C3A>5 per cent C3A > 5 percent |
2.5 3.00 |
2.5 3.00 |
2.5 3.00 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lime saturation factor (LSF) Ratio, AF, minimum |
0.66 to 1.02 0.66 |
0.66 to 1.02 0.66 |
0.8 to 1.02 0.66 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
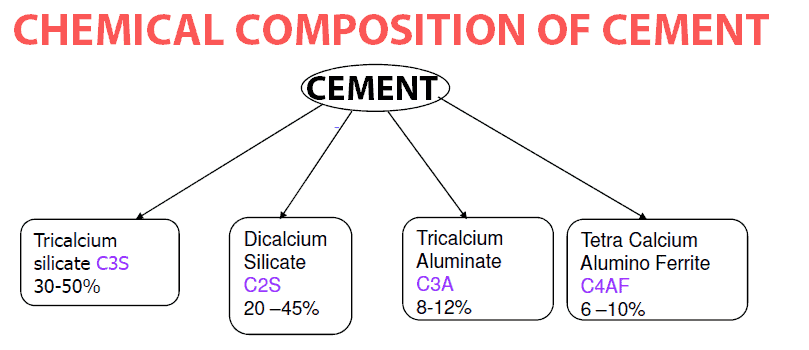
Notes: C3A = 2.65(Al2O3) – 1.69(Fe2O3).
C3S = 4.07(CaO) – 7.6(SiO2) – 6.72(Al2O3) – 1.43(Fe2O3) – 2.85 (SO3), where CaO is the combined lime.
Once you know the class of cement grades category, you will know how it will affect your house’s construction. The degree of cement gets differentiated by the indication terms of the strength. Also, read about the various grades of concrete used in the construction industry.
There are many grades of cement or Types of cement grades that can be used in the construction industry such as 33 Grade Cement, 43 Grade Cement, 53 Grade Cement OPC Cement, etc.
The strength gets further measured as the comprehensive strength, the moulded cement in the standard cube. After 28 days of curing, it gets estimated. The measurements are in Mega-Pascal or N/mm.
Generally, there are three types of cement grades; 33-grade, 43-grade, and 53-grade. Read on to know more about these types of cement that will help you decide on need.
It’s always recommended to take suggestions on What Grades of Cement needs to be used for your building construction from your Hired Architects for designing your House and the structural engineer who designs the structure for the construction.
WHAT IS 33 GRADE CEMENT?

When tested by Blaine’s air permeability method, its fineness shows that it’s not less than 225m/kg.
PROPERTIES OF 33 GRADE CEMENT:
Minimum compressive strength N/mm2:
3 Day: 16 N/mm2.
7 Day: 22 N/mm2.
28 Day: 33 N/mm2.
Chemical Properties:
Loss on ignition: 5.0
Insoluble residue: 2.0
Magnesia MgO: 6.0
The initial setting time for this cement should be 30 minutes and not less, while the final setting time is 600 minutes.
The expansion value is 10mm or 0.8%. Due to the high demand for other cement grades in the market, 33-grade cement has declined. Manufacturers hardly produce it nowadays.
The 33 Grade cement gets used for the general construction of civil work under typical environments, including mass concreting of large areas, cement concreting in plain, and plastering of most prepared surfaces.
If you are planning to start your house construction in Bangalore? and wondering, What would be the Construction cost? One can use our Free “ Cost Calculator tool ” to help you get an approximate budget required.
WHAT IS 43 GRADE CEMENT?

The fineness value of the 43 grade test by Blain’s air permeability method shows that it’s not less than225m/kg.
PROPERTIES OF 43 GRADE CEMENT:
Minimum compressive strength N/mm2:
3 Day: 23 N/mm2.
7 Day: 33 N/mm2.
28 Day: 43 N/mm2.
Chemical Properties:
Loss on ignition: 5.0
Insoluble residue: 2.0
Magnesia MgO: 6.0
The expansion value of this unaerated cement is 10mm or 0.8%. It is not less than 30 minutes for the initial setting time, while the final setting time is at 600 minutes.
The 43-grade cement is standard in countries like India because of its uses. The total production in India accounts for fifty per cent of the total production of cement in the country.
The grade cement gets used in the making of Precasted items like tiles, pipes, and blocks. Civil engineers use it during construction.
The 43 grade is used in concrete work reinforcement, flooring, plastering, and Asbestos products, including pipes and sheets.
WHAT IS 53 GRADE CEMENT?

PROPERTIES OF 43 GRADE CEMENT:
Minimum compressive strength N/mm2:
3 Day: 27 N/mm2.
7 Day: 37 N/mm2.
28 Day: 53 N/mm2.
Chemical Properties:
Loss on ignition: 4.0
Insoluble residue: 2.0
Magnesia MgO: 6.0
The initial setting time is 30 minutes, while the final setting time is more than 600 minutes.
According to Blaine’s air permeability test, the fineness value is 225m/kg, while expansion values range at 10mm when tested with Le -Chaelier method and 0.8% by the autoclave method.
The grade content is known for being rich in quality and has long durability.
The 53-grade cement gets used for the following purposes—pre-pressed contents made of concrete use this cement grade.
Constructors who get involved with the making of Air runways, public roads, and bridges use the grade cement in their work. Further, this cement gets used in the reinforcement of concrete work.
Check the grade of cement before purchasing. It ultimately affects the strength of your structures.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF VARIOUS TYPES OF CEMENT?
| Sl no. | TYPES OF CEMENT | Finene ss (m2 / Kg) Min |
SOUNDNESS | Setting Time (minutes) |
Compressive Strength (MPa) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Le- Chat (max) (mm) |
Autoclave (max) (%) | Initial (min) | Final (max) | 1 D (min) |
3 D (min) |
7 D (min) |
28 D (min) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 33 grade cement OPC (IS 269–1989) |
225 | 10 | 0.8 | 30 | 600 | NS | 16 | 22 | 33 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 43 grade cement OPC (IS 8112– 1989) |
225 | 10 | 0.8 | 30 | 600 | NS | 23 | 33 | Min-43 Max-58 | |||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 53 grade cement OPC (IS 12269– 1987) |
225 | 10 | 0.8 | 30 | 600 | NS | 27 | 37 | 53 | |||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Sulphate Resisting Cement. SRC (IS 12330– 1988) |
225 | 10 | 0.8 | 30 | 600 | NS | 10 | 16 | 33 | |||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Portland Pozzolana Cement. PPC (IS 1489– 1991) Part-I |
300 | 10 | 0.8 | 30 | 600 | NS | 16 | 22 | 33 | |||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Rapid Hardening Cement. PPC (IS 8041– 1990) |
325 | 10 | 0.8 | 30 | 600 | 16 | 27 | NS | NS | |||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Portland Slag Cement. PSC (IS 455–1989) |
225 | 10 | 0.8 | 30 | 600 | NS | 16 | 22 | 33 | |||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Super Sulphated Cement. (IS 6909–1990) |
400 | 5 | NS | 30 | 600 | NS | 15 | 22 | 30 | |||||||||||||||||
| 9 | Low Heat Cement. (IS 12600–1989) |
320 | 10 | 0.8 | 60 | 600 | NS | 10 | 16 | 35 | |||||||||||||||||
| 10 | Masonry Cement. (IS 3466–1988) |
* | 10 | 1.0 | 90 | 1440 | NS | NS | 2.5 | 5.0 | |||||||||||||||||
| 11 | 43-S grade OPC (IS 8112– 1989) |
370 | 10 | 0.8 | 60 | 600 | NS | NS | 37.5 | NS | |||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 53-S grade OPC (IS 12269–1987) |
370 | 10 | 0.8 | 60 | 600 | NS | NS | 37.5 | NS | |||||||||||||||||
CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF VARIOUS TYPES OF CEMENT?
| Sl. No. |
TYPE OF CEMENT | Lime Saturation Factor (%) |
Alumina Iron Ratio (%) Min. |
Insoluble Residue (%) Max. |
Magnesia (%) Max. | Sulphuric Anhydride (%) Max. |
Loss on Ignition (%) Max. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 33 Grade Cement OPC (IS 269–1989) |
0.66 Min. 1.02 Max. |
0.66 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 43 Grade Cement OPC (IS 8112– 1989) |
0.66 Min. 1.02 Max. |
0.66 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 53 Grade Cement OPC (IS 12269– 1987) |
0.80 Min. 1.02 Max. |
0.66 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Sulphate Resisting Cement. SRC (IS 12330– 1988) |
0.66 Min. 1.02 Max. |
NS | 4.0 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Portland Pozzolana Cement. PPC (IS 1489– 1991) Part-I |
NS | NS | X+4 (100- X)/100 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Rapid Hardening Cement. PPC (IS 8041– 1990) |
0.66 Min. 1.02 Max. |
0.66 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 2.5 % Max. When C3A is 5.0 or less. 3.0% Max. When C3A is greater than 5.0 |
5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Portland Slag Cement. PSC (IS 455–1989) |
NS | NS | 4.0 | 8.0 | 3.0% Max. | 5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Super Sulphated Cement. (IS 6909–1990) |
NS | NS | 4.0 | 10.0 | 6.0% Min. | NS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | Low Heat Cement. (IS 12600–1989) | NS | 0.66 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 2.5 % Max. When C3A is 5.0 or less. 3.0% Max. When C3A is greater than 5.0 |
NS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 43-S grade OPC (IS 8112– 1989) |
0.66 Min. 1.02 Max. |
0.66 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 3.5 | LOI 5.0% Max. C3A 10.0 % Max. C3S 45.0% Min. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | 53-S grade OPC (IS 12269–1987) |
0.80 Min. 1.02 Max. |
0.66 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 3.5 | LOI 4.0% Max. C3A 10.0 % Max. C3S 45.0% Min. |
||||||||||||||||||||
TYPE OF CEMENT RECOMENDED BASED ON SO3 level in SOIL?
| CLASS | In SOIL TOTAL SO3% | CONCENTRATION OF SULPHATES EXPRESSED as SO3 | TYPE OF CEMENT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SO3 in 2:1 water : soil extract (g/L) | In groundwater (g/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | > 0.2 | <1.0 | <0.3 | OPC, PSC or PPC | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 0.2 – 0.5 | 1.0-1.9 | 0.3-1.2 | OPC, PSC or PPC SSC or SRC | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 0.5 – 1.0 | 1.9-3.1 | 1.2 – 2.5 | SSC or SRC PSC or PPC | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 1.0 – 2.0 | 3.1-5.0 | 2.5 – 5.0 | SSC or SRC | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | >2.0 | >5.0 | >5.0 | SRC or SSC with a protective coating | |||||||||||||||||||||||
WHAT IS THE NEW TECHNOLOGICAL – CEMENT IMPACT ON OPC CEMENT?
However, the manufacturing of OPC cement is decreasing worldwide because of the popularity of blended cement that has taken over the market.
The mixed cement consumes low energy, has low cost, and results in less environmental pollutions.
The rise in technological advancements has now upgraded the quality of cement in various ways.
Use of limestone by addition of limestone powder into cement paste and mortar gets to increase the strength at the initial stages of running workability.
Concrete is the derived product of the heterogeneous mixture of cement, water, and aggregates.
The critical difference between the new concrete and OPC cement is that concrete is semi-fluid and not powdery like cement. The concrete contribution gets aggregated at 60-70%, the cement of 10-15% with 15-20% of the technological concrete’s water.
The use of modern and advanced equipment in mixture, materials, proportionality, recycling, and durability of cement is adopted by many manufacturers nowadays.
WHAT IS ULTRA HIGH-PERFORMANCE CONCRETE?
The latest new concrete has resulted in ultra-high performance concrete, high-performance concrete, and geopolymer concrete. They have more significance than the 33, 43, and 53 cement grades in regular use today.
High-performance concrete contains recycled materials, which means there is less disposal of equipment.
Some of the concrete materials include ground granulated blast furnace slag, fly ash, and silica fume. The reduction in pollution gets impacted by the use of such materials hence results in environmental-free surroundings.
There is a reduction in the creation of carbon dioxide emissions and energy consumption.
WHAT ARE THE PROPERTIES OF CEMENT?
The new cement, due to technology, is durable. The life span is measured to be hundreds of years than decades. The use of fly ash will save many in years to come from burning coal and other waste by-products for industries.
When compared to standard cement, their corrosion resistance is better; the compressive is equal or higher with high tensile strengths, resistant levels to fire are high, and rapid curing strength gain.
BSI and Ductal are the new used technological concretes. Ductal is denser than BSI, which has higher tensile and flexural strength than the standard cement mixture. The fibre-reinforced concrete gets combined with dry premixed components.
Ductal uses organic fibers and steel to make the concrete more durable than BSI. They are resistant to earthquakes and are used to make bridges, nuclear containment structures, and tunnels.
The concrete materials have a low cost of maintenance, low porosity, water-resistant, and chemical-resistant. They are also resistant to saltwater, which is known to be highly corrosive.
What are the different Types of Cement or Grades of Cement used in construction?
There are different grades of cement used in the construction industry like 33 Grade Cement, 43 Grade Cement, 53 Grade Cement, and advanced cement grades are manufactured as per the required use.
What is 33 Grade Cement and Uses of 33 Grade Cement in construction?
A 33 grade Cement archives a Minimum compressive strength of 33 N/mm2 after 28days. A 33 Grade cement is used in Plain cement concrete (PCC) where it’s not subjected to stress.
What is 43 Grade Cement and Uses of 43 Grade Cement in construction?
A 43 grade Cement archives a Minimum compressive strength of 43 N/mm2 after 28days. A 43 Grade is used in all kinds of reinforced works such as reinforcement, cement pipes, plaster, flooring etc.
What is 53 Grade Cement and Uses of 53 Grade Cement in construction?
A 53 grade Cement archives a Minimum compressive strength of 53 N/mm2 after 28days. A 53 Grade Cement construction of Air runways, public roads, and bridge
What is the Minimum compressive strength of 33 Grade 43 Grade 53 Grade Cement?
The Minimum compressive strength after 28 days for 33 Grade cement is 33 N/mm2, 43 Cement Grade is 43 N/mm2, 53 Cement Grade is 53 N/mm2 after 28 days.